Question 1 (a)
- Profit per unit = Demand(Price) - ATC
Question 1 (d)

Formula
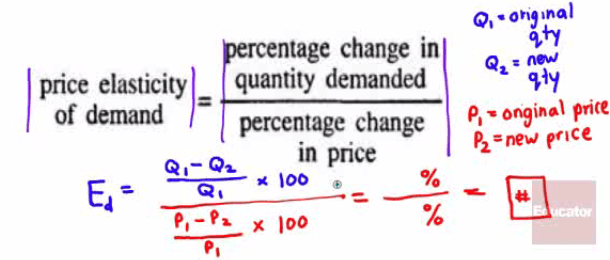
How to remember
- Queen is greater than the Princess
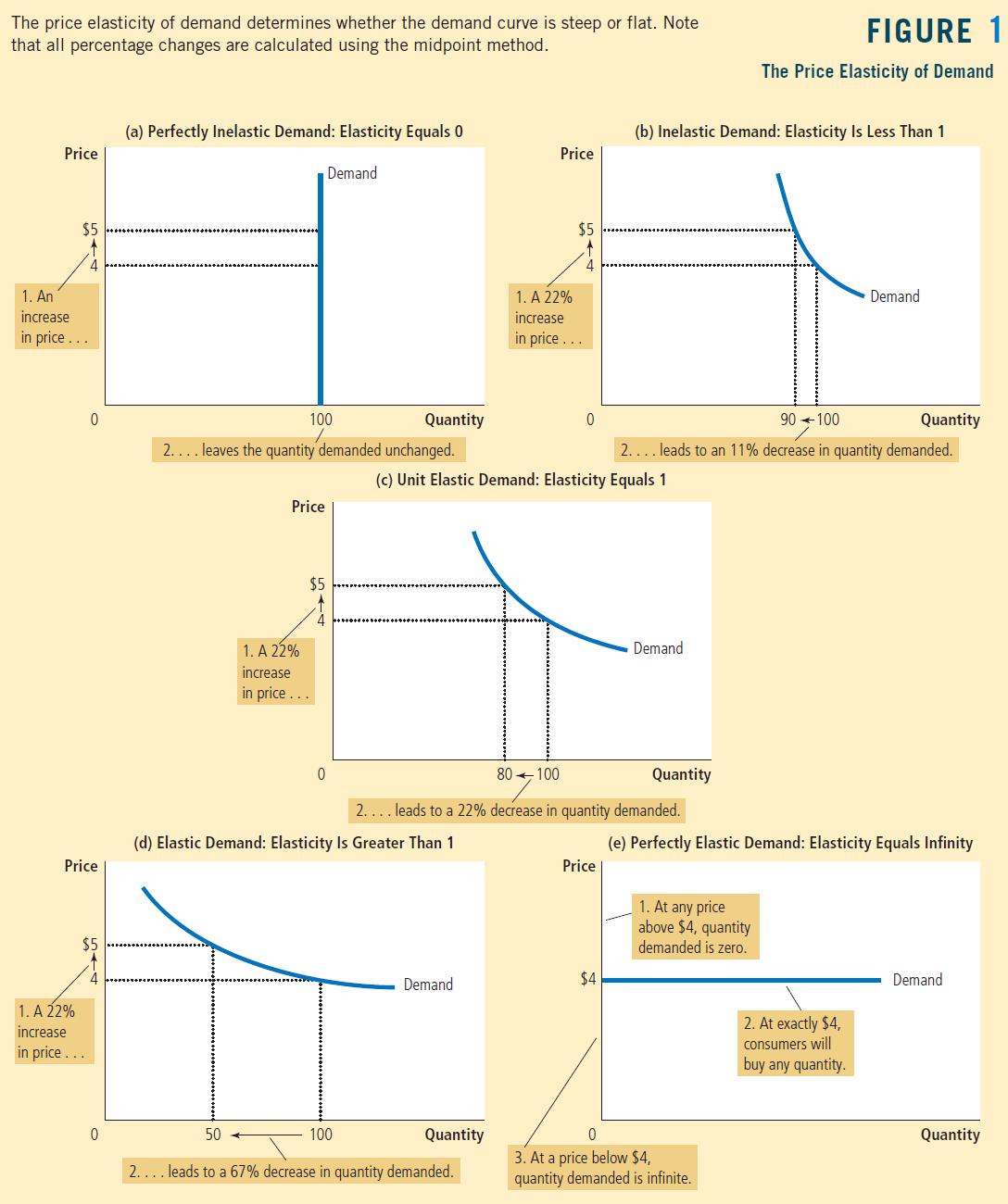
Question 1 (e)
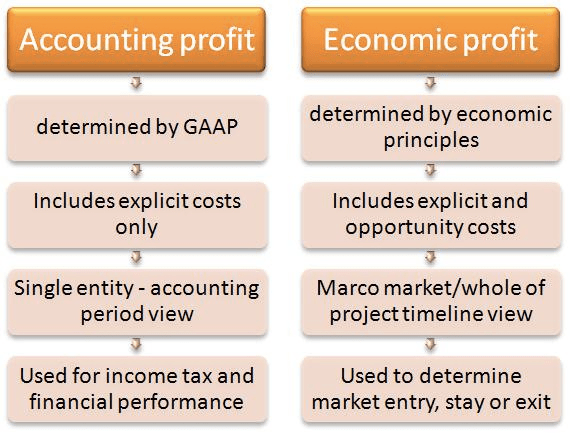
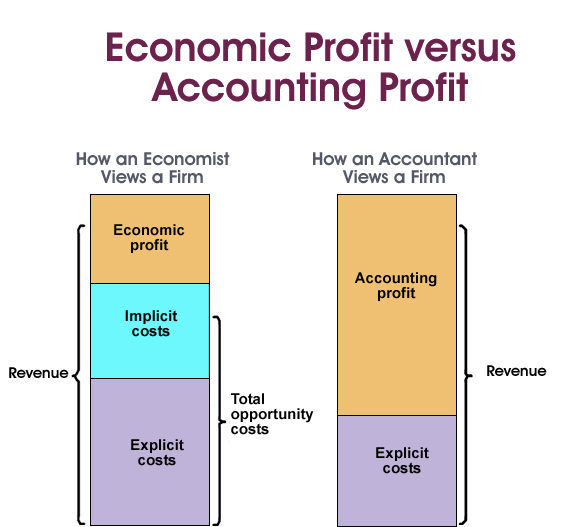
Accounting Profit ≥ Economic Profit

Question 1 (f)
- Profit = Revenue - Cost
Question 2 (a)
Graph for a typical firm should include
Marginal Cost
Marginal Revenue
Demand(Price)
Average Total Cost
Profit = (Price - ATC)* Quantity
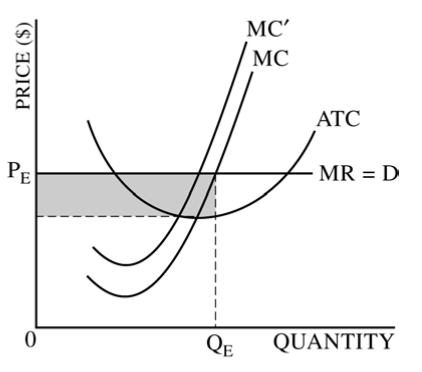
Question 2 (c)
A typical labor supply and demand graph should include
Marginal Factor Cost: Horizontal
Marginal Revenue Product (Marginal Product of Labor): Downward sloping
x-axis: Quantity of Labor
y-axis: Wage Rate
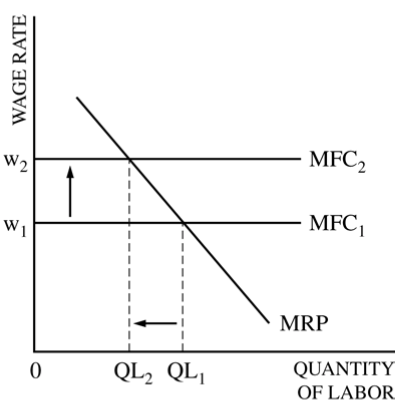
Question 3 (a)
Negative Social Externality
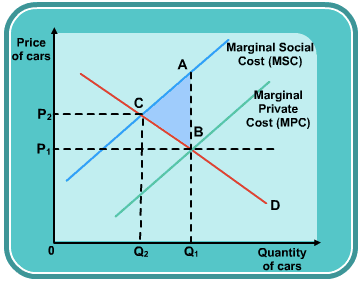
Positive Social Externality
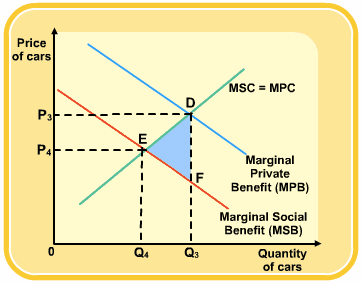
Question 3 (b)
- A lump-sum tax will not change the deadweight loss, since the MC will not change